Patellar Clunk Syndrome Treatment
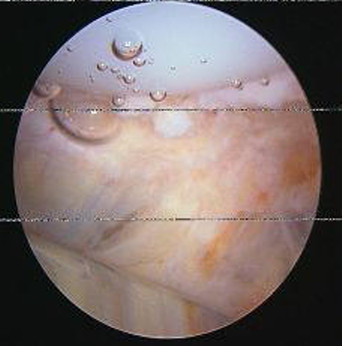
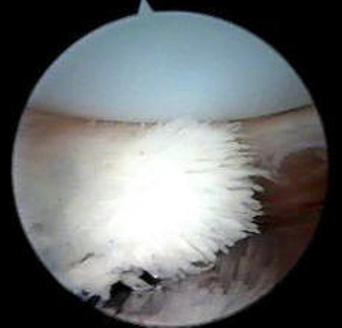
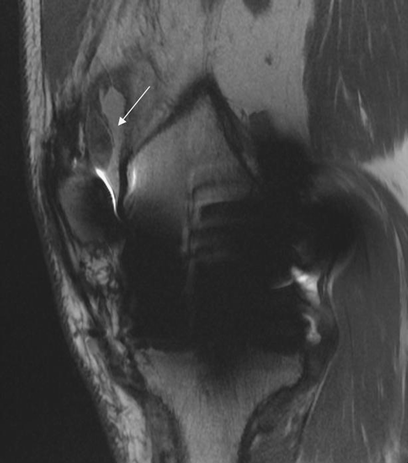
Patellar clunk syndrome treatment. While this was done in an open fashion in the early days of PS TKR today arthroscopic treatment is indicated. Magnetic resonance imaging has been used to demonstrate a fibrous soft tissue nodule proximal to the patella in 75 912 of patients with suspected patellar clunk. They suggested surgeons include the potential for clunk or crepitus while providing informed consent to patients who have had prior TKAs.
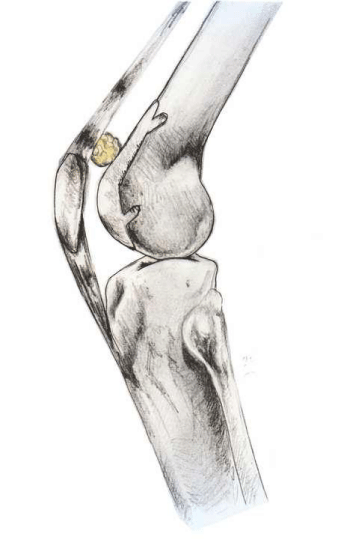
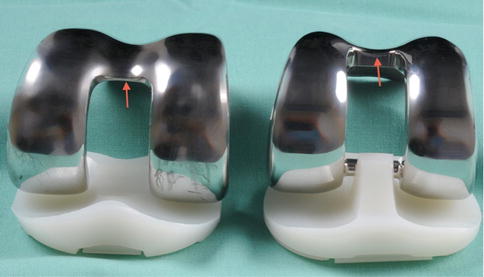
We identified 15 knees in 15 patients with patellar clunk and 10 knees in 9 patients with patellofemoral synovial hyperplasia which were treated with arthroscopy after TKA. The chances of getting a nodule and a clunk are much lower with the design of the new implant. Patellar clunk syndrome occurs when a fibrous nodule develops just proximal to the patellar button.
Four femoral components were in 5 degrees flexion. Patellar Clunk Syndrome is a painful palpable clunk that can occur at the patellofemoral articulation of a posterior stabilized TKA caused by a fibrous nodule of scar tissue. Since most patients with crepitus have minimal symptoms they require no treatment.
MRI helps confirm the clinical diagnosis of patellar clunk. Home treatment options Because patellofemoral syndrome often results from overuse and overactivity resting the affected joint can often help treat the underlying problem. Arthroscopic treatment of patellar clunk.
When the patella shifts slightly out of place it can cause a knee clunking sensation as it shifts up and down the patella groove. Can you treat patellar clunk syndrome. In most cases treatment is initially conservative.
Recurrence can be treated by open resection despite the higher risk of complications with this method. With this new implant it takes much more knee flexion for the patella to drop into the notch in the surface of the femur. Diagnosis can be made clinically with the presence of a painful palpable pop or catch as knee extends 40 of flexion.
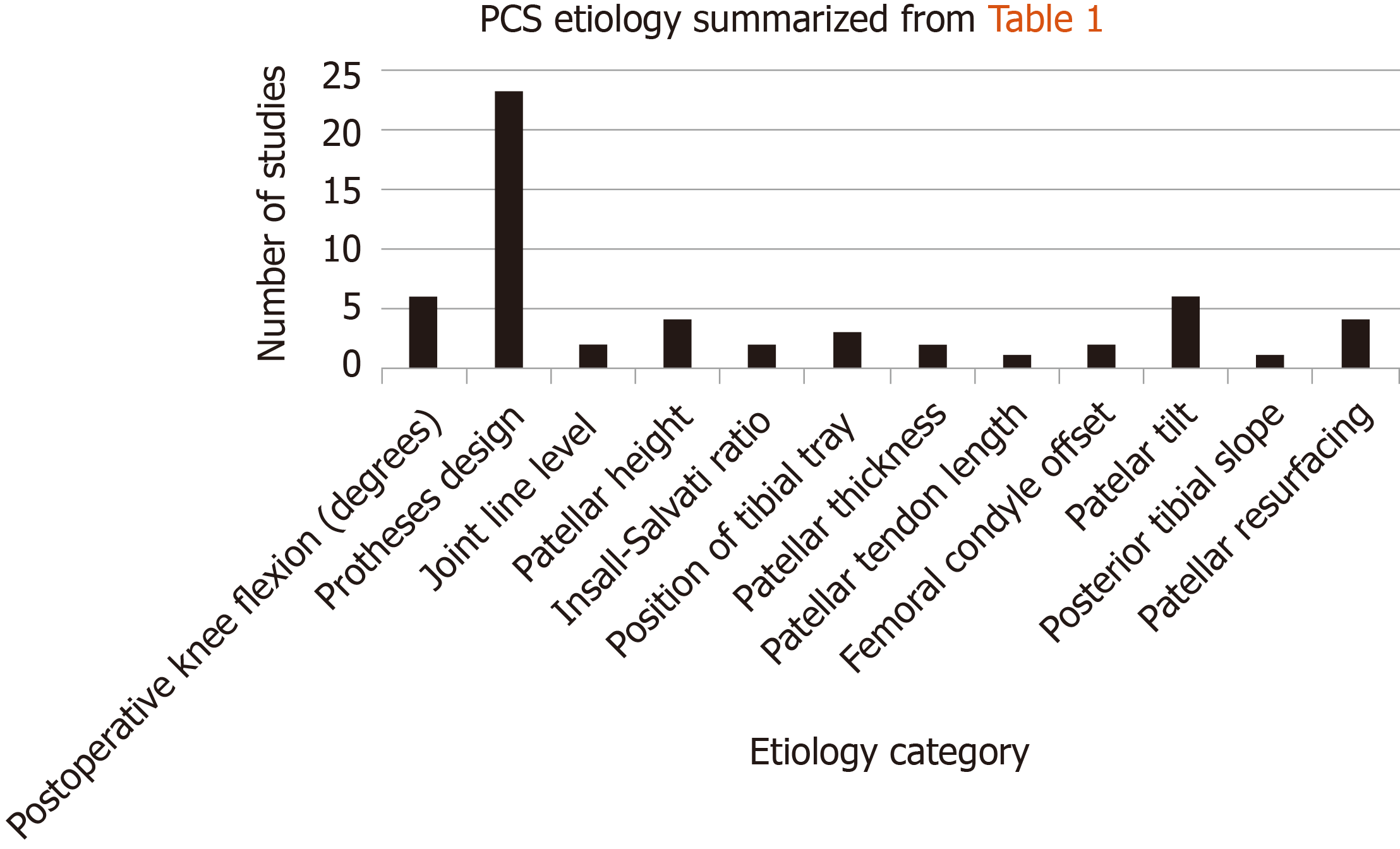
This is a syndrome which occurs when a fibrous nodule forms on the joint capsule just above the patella. The purpose of this control-matched retrospective study is to report long-term functional outcomes of arthroscopic treatment for patellar clunk syndrome by a single surgeon at a single institution using a single implant design and to identify technical and radiographic risk factors associated with PCS.
In eight patients this lead to operative treatment with arthroscopic debridement.
The chances of getting a nodule and a clunk are much lower with the design of the new implant. Since most patients with crepitus have minimal symptoms they require no treatment. The purpose of this control-matched retrospective study is to report long-term functional outcomes of arthroscopic treatment for patellar clunk syndrome by a single surgeon at a single institution using a single implant design and to identify technical and radiographic risk factors associated with PCS. Patellar Clunk Syndrome is a painful palpable clunk that can occur at the patellofemoral articulation of a posterior stabilized TKA caused by a fibrous nodule of scar tissue. We performed a retrospective review of 25 patients who underwent arthroscopic debridement after primary TKA to treat the patellar clunk syndrome 15 knees or patellofemoral synovial hyperplasia 10 knees. All patients had a primary diagnosis of osteoarthritis. Diagnosis can be made clinically with the presence of a painful palpable pop or catch as knee extends 40 of flexion. Treatment is observation for patients with. This is a complication of Total Knee Replacement and once this develops the Knee starts making a loud clunk.
Can you treat patellar clunk syndrome. At about 40 degrees of flexion this lump gets trapped between the anterior flange of the femoral component and hence the clunk. We identified 15 knees in 15 patients with patellar clunk and 10 knees in 9 patients with patellofemoral synovial hyperplasia which were treated with arthroscopy after TKA. Treatment is observation for patients with. With this new implant it takes much more knee flexion for the patella to drop into the notch in the surface of the femur. In eight patients this lead to operative treatment with arthroscopic debridement. While this was done in an open fashion in the early days of PS TKR today arthroscopic treatment is indicated.
































Post a Comment for "Patellar Clunk Syndrome Treatment"