Physicians May Withdraw Or Withhold Aggressive, Life-sustaining Treatment Under Which Condition?
Physicians may withdraw or withhold aggressive, life-sustaining treatment under which condition?. When a person may or has become dependent on such a treatment decisions may need to be made about whether to withhold or withdraw the treatment not start it or stop using it. This article summarizes the American. Advance Directiveslegislation.
A patient who decides not to use life-sustaining treatment or who decides not to continue using a life-sustaining treatment is not committing suicide. 1 Any adult person may execute a directive directing the withholding or withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in a terminal condition or permanent unconscious condition. 1Health Care Practice Group Adler Pollock Sheehan Incorporated Providence Rhode Island.
Withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining therapies is ethical and medically appropriate in some circumstances. A physician may consider withholding or withdrawing life sustaining treatment from a patient in instances of a terminal condition or permanent unconscious condition. Directive to withhold or withdraw life-sustaining treatment.
Your Answer The patient knows all of the options and refuses treatment. There are a few scenarios that a physician may withdraw or withhold aggressive life sustaining treatment. Life-sustaining therapies are frequently withheld or withdrawn.
Another scenario is when the healthcare team decides that the patient already is not benefitting and actually becoming. - The state allows physician-assisted suicide. Withholding and withdrawing life-sustaining treatment are considered to be equal acts.
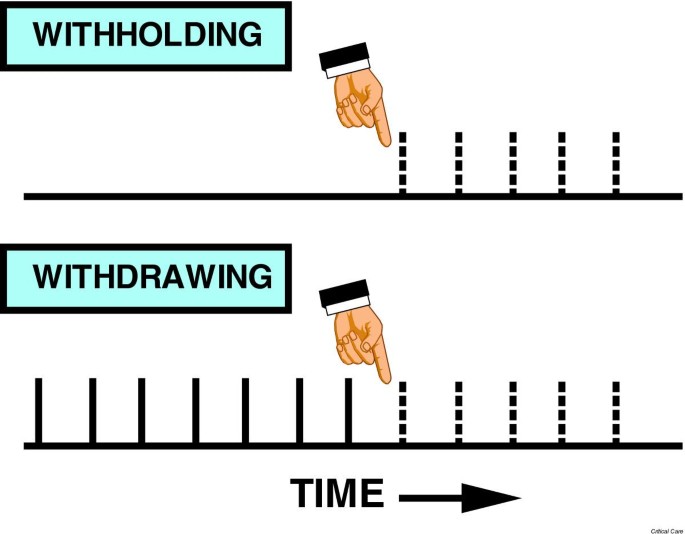
In emergency medicine a significant difference rightfully persists between the withholding and withdrawal of life-sustaining medical treatment. Wollin DA1 Avanzato J. Withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining therapies is ethical and medically appropriate in these circumstances.
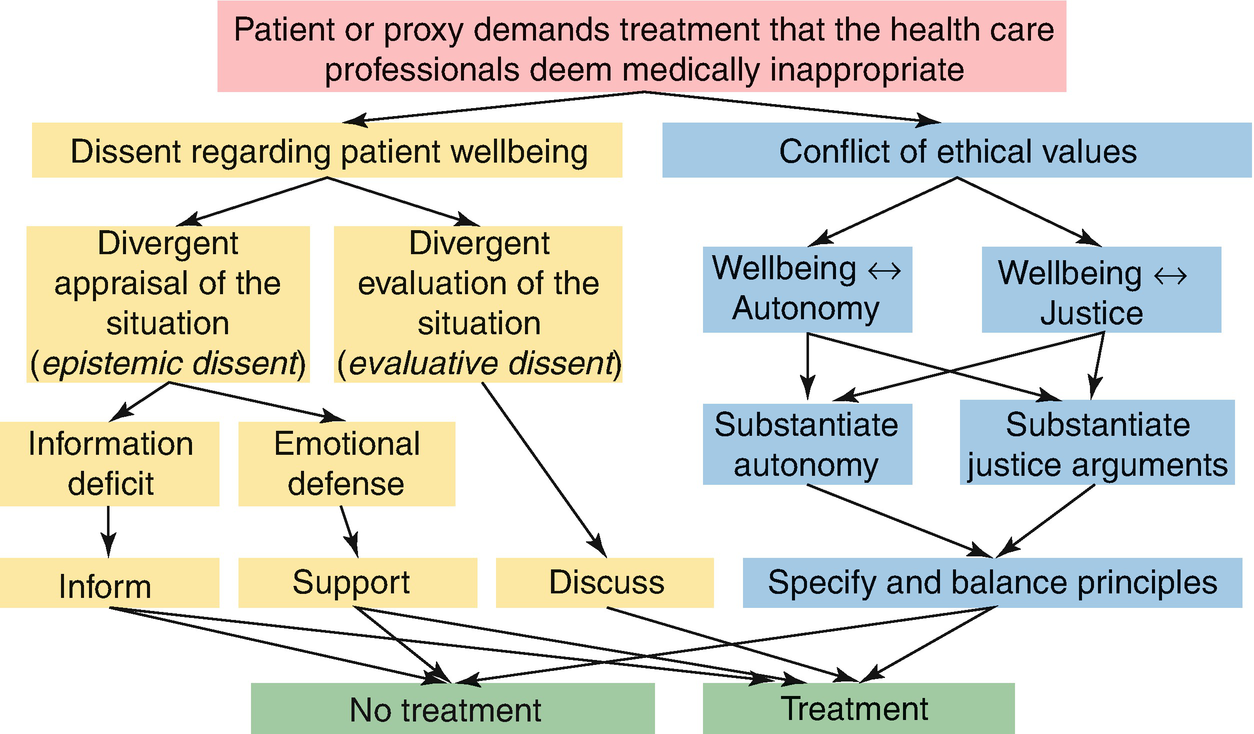
Physicians may withdraw or withhold aggressive life-sustaining treatment under which condition. When an intervention no longer helps to achieve the patients goals for care or desired quality of life it is ethically appropriate for physicians to withdraw it.
The justification for this difference stems in part from the nature of emergency medical practice and the unique manner in.
Physicians obligations to withhold or withdraw life-sustaining medical treatment. 1 Any adult person may execute a directive directing the withholding or withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in a terminal condition or permanent unconscious condition. When a person may or has become dependent on such a treatment decisions may need to be made about whether to withhold or withdraw the treatment not start it or stop using it. Withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining therapies is ethical and medically appropriate in some circumstances. This article summarizes the American. Physicians may withdraw or withhold aggressive life-sustaining treatment under which condition. Withholding and withdrawing life-sustaining treatment are considered to be equal acts. A patient who decides not to use life-sustaining treatment or who decides not to continue using a life-sustaining treatment is not committing suicide. Ethically and legally the decision to withhold or withdraw therapies is guided by the principle of autonomy.
Wollin DA1 Avanzato J. This article summarizes the American. Conclusions A large percentage of internists would be unwilling to adhere to some of patients wishes to withhold or withdraw life-sustaining treatment. Another scenario is when the healthcare team decides that the patient already is not benefitting and actually becoming. First and most absolute is that when a patient requests that he or she wants the treatment to be withheld or withdrawn. A patient who decides not to use life-sustaining treatment or who decides not to continue using a life-sustaining treatment is not committing suicide. Physicians may withdraw or withhold aggressive life-sustaining treatment under which condition.


































Post a Comment for "Physicians May Withdraw Or Withhold Aggressive, Life-sustaining Treatment Under Which Condition?"